Unveiling the Gastric Problems: Common Symptoms and Their Causes
Posted on : March 07, 2024
Gastric problems, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain, can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the symptoms and their underlying causes is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this article, we'll explore seven common symptoms of gastric problems and delve into their potential causes, providing valuable insights for better health and well-being.
-
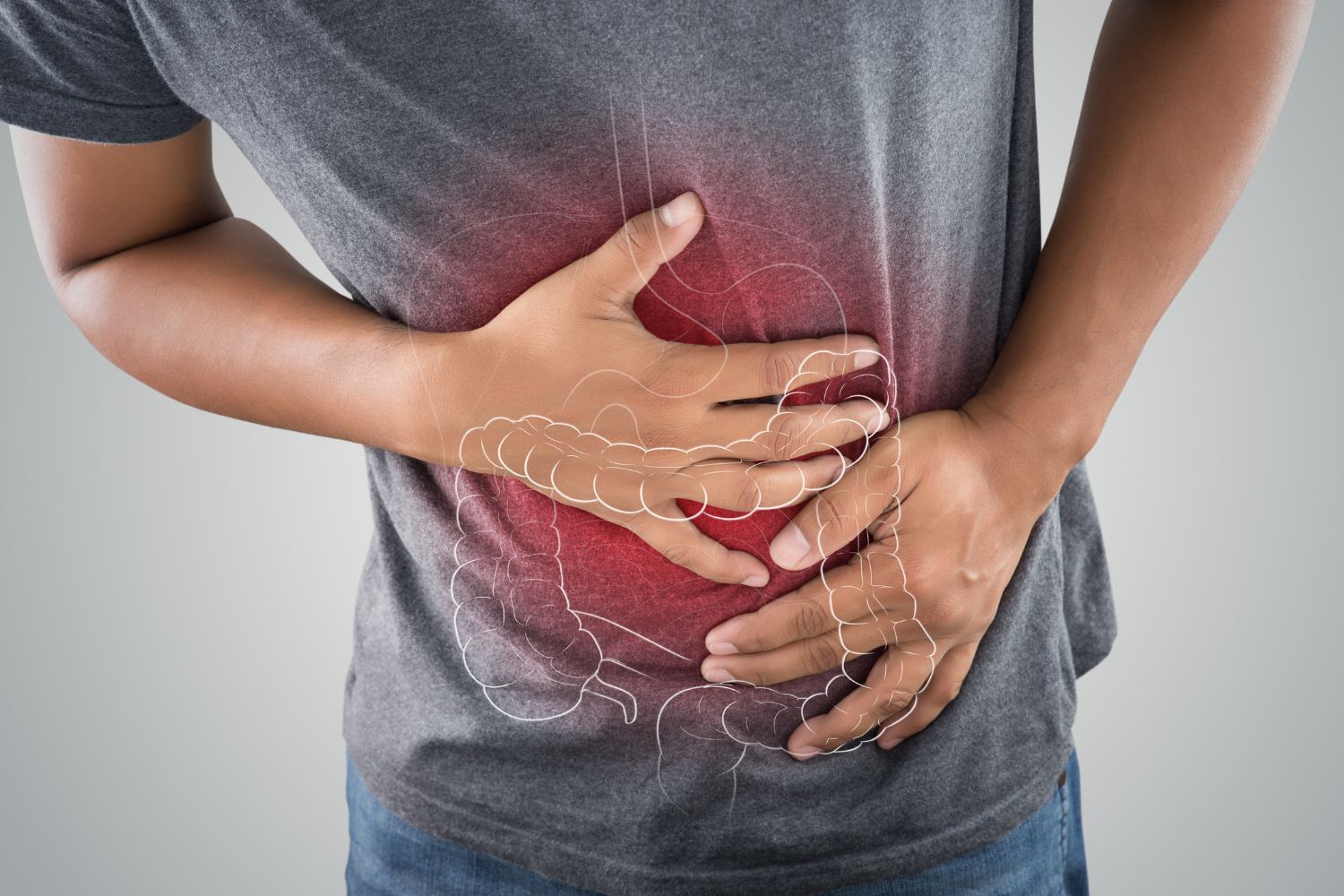
Abdominal Pain: Abdominal pain is a hallmark symptom of various gastric issues, including gastritis, ulcers, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The pain may vary in intensity and location, ranging from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations. Gastric ulcers, caused by the erosion of the stomach lining, often result in a burning pain in the upper abdomen. GERD, characterized by the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, can cause a burning sensation in the chest, known as heartburn.
-
Bloating and Gas: Excessive gas and bloating are common complaints associated with gastric problems. Gas can accumulate in the digestive tract due to factors such as swallowing air, bacterial fermentation of undigested food, or impaired digestion. Bloating, characterized by a feeling of fullness or tightness in the abdomen, often accompanies excessive gas production. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) are frequently implicated in chronic bloating and gas.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are symptoms that can occur in various gastric disorders, including gastritis, gastroparesis, and peptic ulcers. Gastritis, inflammation of the stomach lining, can trigger nausea and vomiting, particularly after meals or when the stomach is empty. Gastroparesis, a condition characterized by delayed stomach emptying, may lead to persistent nausea and vomiting, especially after consuming solid foods. Peptic ulcers, open sores in the stomach or duodenum, can cause nausea and vomiting if they irritate the stomach lining.
-
Indigestion (Dyspepsia): Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, encompasses a range of symptoms, including discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, bloating, and a feeling of fullness during or after meals. It can occur as a result of various factors, such as overeating, eating too quickly, or consuming spicy or fatty foods. Gastric disorders like GERD, gastritis, and peptic ulcers can also manifest as indigestion. Persistent or recurrent indigestion warrants medical evaluation to identify and address the underlying cause.
-
Acid Reflux: Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation in the chest (heartburn) and a sour taste in the mouth. It is a common symptom of GERD, a chronic condition characterized by frequent episodes of acid reflux. Certain dietary and lifestyle factors, such as consuming acidic or fatty foods, smoking, and obesity, can exacerbate acid reflux. In some cases, structural abnormalities like a hiatal hernia may contribute to the development of GERD.
-
Loss of Appetite: A decreased appetite, or anorexia, can be a symptom of various gastric disorders, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Gastritis, characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining, can lead to a loss of appetite due to discomfort or nausea associated with eating. Peptic ulcers, particularly those located in the stomach, can cause a feeling of early satiety or discomfort after meals, leading to reduced food intake. Inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, can affect the entire digestive tract and cause appetite loss.
-
Changes in Bowel Habits: Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or alternating episodes of both, can indicate underlying gastric issues. Conditions like IBS, characterized by abdominal pain and altered bowel habits without any detectable structural abnormalities, often present with diarrhea, constipation, or a combination of both. Inflammatory conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can cause diarrhea, often accompanied by abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and weight loss. Constipation may occur due to factors such as inadequate fiber intake, dehydration, or certain medications.
Gastric problems can manifest in various ways, ranging from abdominal pain and bloating to acid reflux and changes in bowel habits. Identifying the symptoms and understanding their underlying causes are essential steps in managing gastric disorders effectively. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and treatment. With the right approach, many gastric issues can be effectively managed, allowing for improved quality of life and overall well-being.
Disclaimer: The content on this blog serves educational, informational, and awareness purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Consult your doctor/healthcare provider before acting on any information provided. Relying on the blog content is at your own risk. SCG Healthcare Private Limited bears no responsibility for any consequences resulting from the use of this information.